Merge sort is one of the most efficient sorting algorithms. It works on the principle of Divide and Conquer. Merge sort repeatedly breaks down a list into several sublists until each sublist consists of a single element and merging those sublists in a manner that results into a sorted list.
A merge sort works as follows:
Top-down Merge Sort Implementation:
The top-down merge sort approach is the methodology which uses recursion mechanism. It starts at the Top and proceeds downwards, with each recursive turn asking the same question such as “What is required to be done to sort the array?” and having the answer as, “split the array into two, make a recursive call, and merge the results.”, until one gets to the bottom of the array-tree.
Example: Let us consider an example to understand the approach better.
-
Divide the unsorted list into n sublists, each comprising 1 element (a list of 1 element is supposed sorted).

Top-down Implementation
-
Repeatedly merge sublists to produce newly sorted sublists until there is only 1 sublist remaining. This will be the sorted list.
Merging of two lists done as follows:
The first element of both lists is compared. If sorting in ascending order, the smaller element among two becomes a new element of the sorted list. This procedure is repeated until both the smaller sublists are empty and the newly combined sublist covers all the elements of both the sublists.

Merging of two lists
Implementation Of Merge Sort
// example of merge sort in C/C++
// merge function take two intervals
// one from start to mid
// second from mid+1, to end
// and merge them in sorted order
void merge(int *Arr, int start, int mid, int end) {
// create a temp array
int temp[end - start + 1];
// crawlers for both intervals and for temp
int i = start, j = mid+1, k = 0;
// traverse both arrays and in each iteration add smaller of both elements in temp
while(i <= mid && j <= end) {
if(Arr[i] <= Arr[j]) {
temp[k] = Arr[i];
k += 1; i += 1;
}
else {
temp[k] = Arr[j];
k += 1; j += 1;
}
}
// add elements left in the first interval
while(i <= mid) {
temp[k] = Arr[i];
k += 1; i += 1;
}
// add elements left in the second interval
while(j <= end) {
temp[k] = Arr[j];
k += 1; j += 1;
}
// copy temp to original interval
for(i = start; i <= end; i += 1) {
Arr[i] = temp[i - start]
}
}
// Arr is an array of integer type
// start and end are the starting and ending index of current interval of Arr
void mergeSort(int *Arr, int start, int end) {
if(start < end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
mergeSort(Arr, start, mid);
mergeSort(Arr, mid+1, end);
merge(Arr, start, mid, end);
}
}// example of merge sort in Java
// merge function take two intervals
// one from start to mid
// second from mid+1, to end
// and merge them in sorted order
void merge(int Arr[], int start, int mid, int end) {
// create a temp array
int temp[] = new int[end - start + 1];
// crawlers for both intervals and for temp
int i = start, j = mid+1, k = 0;
// traverse both arrays and in each iteration add smaller of both elements in temp
while(i <= mid && j <= end) {
if(Arr[i] <= Arr[j]) {
temp[k] = Arr[i];
k += 1; i += 1;
}
else {
temp[k] = Arr[j];
k += 1; j += 1;
}
}
// add elements left in the first interval
while(i <= mid) {
temp[k] = Arr[i];
k += 1; i += 1;
}
// add elements left in the second interval
while(j <= end) {
temp[k] = Arr[j];
k += 1; j += 1;
}
// copy temp to original interval
for(i = start; i <= end; i += 1) {
Arr[i] = temp[i - start]
}
}
// Arr is an array of integer type
// start and end are the starting and ending index of current interval of Arr
void mergeSort(int Arr[], int start, int end) {
if(start < end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
mergeSort(Arr, start, mid);
mergeSort(Arr, mid+1, end);
merge(Arr, start, mid, end);
}
}# example of merge sort in Python
# merge function take two intervals
# one from start to mid
# second from mid+1, to end
# and merge them in sorted order
def merge(Arr, start, mid, end) :
# create a temp array
temp[] = [0] * (end - start + 1)
# crawlers for both intervals and for temp
i, j, k = start, mid+1, 0
# traverse both lists and in each iteration add smaller of both elements in temp
while(i <= mid and j <= end) :
if(Arr[i] <= Arr[j]) :
temp[k] = Arr[i]
k += 1; i += 1
else :
temp[k] = Arr[j]
k += 1; j += 1
# add elements left in the first interval
while(i <= mid) :
temp[k] = Arr[i]
k += 1; i += 1
# add elements left in the second interval
while(j <= end) :
temp[k] = Arr[j]
k += 1; j += 1
# copy temp to original interval
for i in range (start, end+1) :
Arr[i] = temp[i - start]
# Arr is an array of integer type
# start and end are the starting and ending index of current interval of Arr
def mergeSort(Arr, start, end) {
if(start < end) :
mid = (start + end) / 2
mergeSort(Arr, start, mid)
mergeSort(Arr, mid+1, end)
merge(Arr, start, mid, end)Bottom-Up Merge Sort Implementation:
The Bottom-Up merge sort approach uses iterative methodology. It starts with the “single-element” array, and combines two adjacent elements and also sorting the two at the same time. The combined-sorted arrays are again combined and sorted with each other until one single unit of sorted array is achieved.
Example: Let us understand the concept with the following example.
- Iteration (1)
![Bottom-up Iteration 1]()
Merge pairs of arrays of size 1
- Iteration (2)
![Bottom-up Iteration 2]()
Merge pairs of arrays of size 2
- Iteration (3)
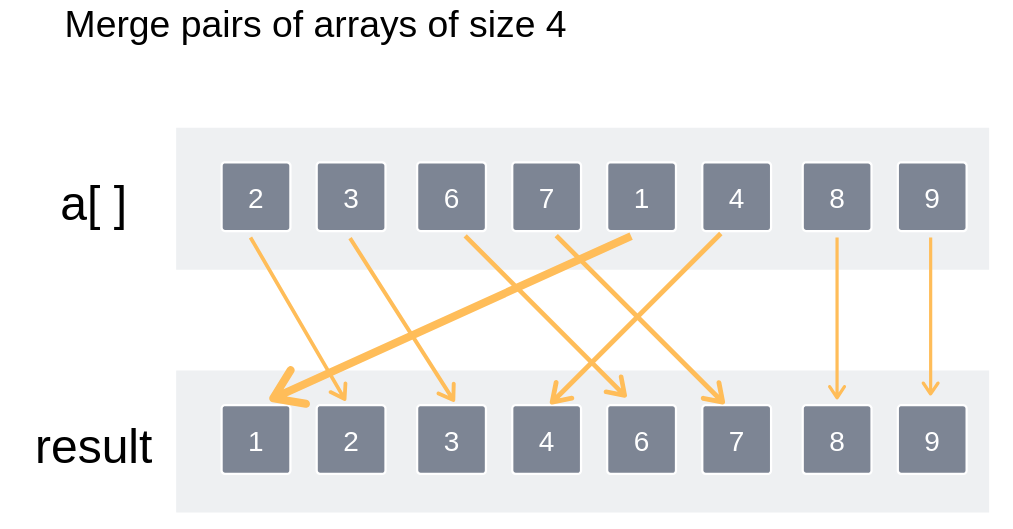
![Bottom-up implementation]()
Merge pairs of arrays of size 4
Thus the entire array has been sorted and merged.






















 Video Courses
Video Courses






 App
App







