Bit Manipulation
Go to ProblemsUnderstanding Data Types
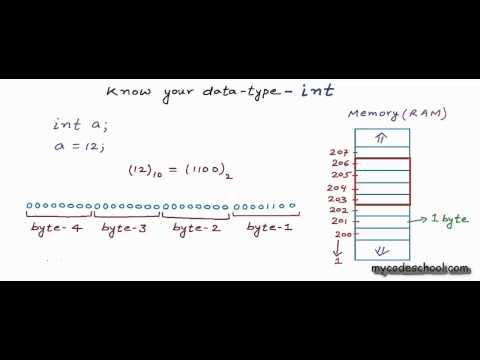
As we have already seen in the previous lesson, the computer only understands binary i.e. the data stored in the Memory (RAM) is in binary form.
Here’s how we can imagine the Memory in a computer to be like the following.
| Address | Binary number stored ( 1byte) |
|---|---|
| 105 | 01001001 |
| 106 | 11101011 |
| 107 | 00000001 |
We can see that each of the bytes has got a unique address.
Each digit of a byte is called a bit. A bit can only have two values either 0 or 1. Also 1 byte = 8 bits
When we declare a variable we reserve some amount of memory to store some data. The amount of memory to be reserved depends on the Data Type , The compiler and the machine architecture. Now let’s look at the types of Data Type which are present and the amount of memory which is reserved for them.
The data types are basically divided into 3 types.
1. Primitive data type:
- The data types which are built in data types and a user can use them directly to define a variable directly are called Primitive data types.
- Examples: Integer , Character, Boolean , Floating Point , Double , Void ( Valueless) , Wide Character.
2. Derived data type:
- The data types which are derived from primitive data types are known as Derived data types.
- Examples:Function , Array , Pointer , Reference
3. Abstract or User defined data type:
- The data types which are defined by the user itself are known as Abstract data types
- Examples: Class , Structure , Union , Enumeration , Typedef defined Datatype.
The below table shows the size and range of primitive data types.
| Data Type | Size (in bytes) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| int | 4 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| float | 4 | |
| double | 8 | |
| char | 1 | -128 to 127 |
Using the above table we can pretty much calculate the size of any program. Here are some of the examples.
| Snippet | Size (in bytes) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
int arr[4]; |
16 | Each element of the array takes 4 bytes. 4 x 4 = 16. |
int a=5;char c=’a’;
|
5 | int takes 4 bytes, char takes 1. |
struct student{ char c; char d; int a;}
|
8 | The intuitive answer might be 6 but due ‘Structure Padding’ The answer comes to 8. It's a very commonly asked question in interviews. You can read more about it. |
Bit Manipulation Problems
| Problem | Score | Companies | Time | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of 1 Bits | 200 |
|
8:47 | |
| Trailing Zeroes | 200 |
|
14:58 | |
| Reverse Bits | 225 |
|
23:50 | |
| Divide Integers | 250 |
|
68:08 | |
| Different Bits Sum Pairwise | 300 |
|
51:30 |
| Problem | Score | Companies | Time | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min XOR value | 200 |
|
37:42 | |
| Count Total Set Bits | 200 |
|
65:54 | |
| Palindromic Binary Representation | 200 |
|
64:40 | |
| XOR-ing the Subarrays! | 200 |
|
34:36 |
| Problem | Score | Companies | Time | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Number | 275 |
|
11:53 | |
| Single Number II | 275 |
|
39:22 |