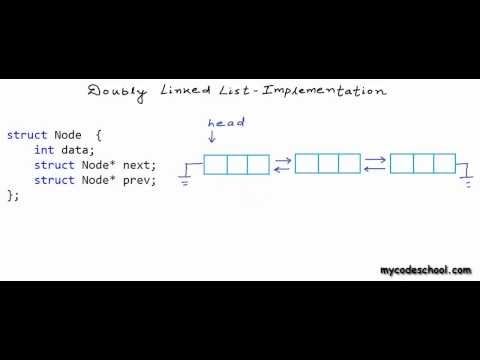
Each node in a list consists of at least three parts:
1. Data
2. Pointer to the previous node
3. pointer to the next node
An example of a doubly linked list node with an integer data.
// A Doubly Linked list node
struct DoublyLinkedList
{
int val;
struct DoublyLinkedList *next, *pre;
};// Doubly Linked list class
class DoublyLinkedList
{
// head of list
Node head;
// Node class
class Node
{
int val;
Node next, pre;
// Constructor to create a new node
Node(int v) {
val = v;
}
}
}# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, v):
self.val = v # Assign value
self.next = None # Initialize next as null
# Doubly Linked List class
class DoublyLinkedList:
# Function to initialize the Linked List
def __init__(self):
self.head = None



















 Video Courses
Video Courses






 App
App







