A linked list is a linear data structure where each element is a separate object.
Linked list elements are not stored at contiguous location; the elements are linked using pointers.
Each node of a list is made up of two items - the data and a reference to the next node. The last node has a reference to null. The entry point into a linked list is called the head of the list. It should be noted that head is not a separate node, but the reference to the first node. If the list is empty then the head is a null reference.
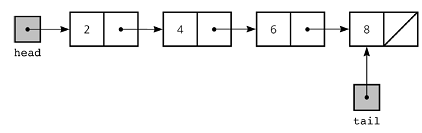
Linked List Representation
An example of a linked list node with an integer data.
// Linked list example in C/C++
// A linked list node
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
};// Linked list example in Java
// Linked list class
class ListNode
{
// head of list
Node head;
// Node class
class Node
{
int val;
Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
Node(int v) {
val = v;
}
}
}# Linked list example in Python
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, v):
self.val = v # Assign value
self.next = None # Initialize next as null
# Linked List class
class ListNode:
# Function to initialize the Linked List
def __init__(self):
self.head = None



















 Video Courses
Video Courses






 App
App







