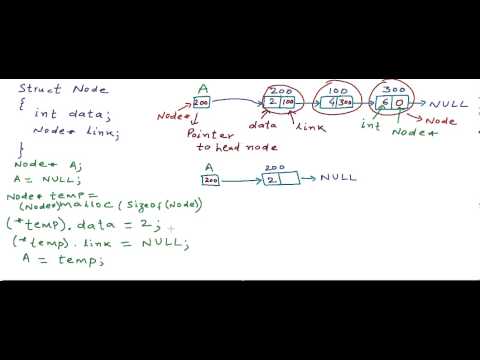
Each node in a list consists of at least two parts:
1. Data
2. Pointer to the next node
In C/C++, we can represent a node of Linked List using structures or classes.
In Java and Python, Linked List can be represented as a class and a Node as a separate class. The LinkedList class contains a reference of Node class type.
An example of a linked list node with an integer data.
// A linked list node
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
};// Linked list class
class ListNode
{
// head of list
Node head;
// Node class
class Node
{
int val;
Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
Node(int v) {
val = v;
}
}
}# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, v):
self.val = v # Assign value
self.next = None # Initialize next as null
# Linked List class
class ListNode:
# Function to initialize the Linked List
def __init__(self):
self.head = NoneWalkthrough Example :




















 Video Courses
Video Courses






 App
App







