IoT Interview Questions
What is IoT (Internet of Things)
The term IoT (Internet of Things) was coined by Kevin Ashton in 1999. It is referred to as a network comprised of interconnected physical objects (referred to as "things") worldwide that are capable of collecting and exchanging data without human interaction. These devices contain embedded systems (software, electronics, networks, and sensors) that are able to collect data about the surrounding environment, transmit data over a network, respond to remote commands, or take actions based on data collected. There are many IoT devices or things available today, including wearables, implants, vehicles, machinery, smartphones, appliances, computing systems, or any other item that can send and receive data.

Cloud-based storage and computing, Cyber-Physical Systems, and big data networks can all be integrated with IoT. The IoT primarily focuses on expanding internet connectivity from standard devices (such as computers, mobile phones, or tablets) to relatively dumb ones like toasters. It turns old "dumb" devices into "smart" ones by making them able to transmit data over the internet, facilitating communication with people and other IoT-enabled devices.
IoT Interview Questions for Freshers
1. What do you mean by replication?
In replication, data is synchronized between two or more servers. This is a method of storing the same data on more than one site or server. This feature allows data to be accessed seamlessly even during server downtimes or heavy traffic. Users gain consistent access to data while not interfering with or slowing down those of other users.

Replication of data is more than just a backup. A publisher is considered to be the server that originates the data, and a subscriber is the one where it is replicated. Data replication involves the publisher synchronizing its transaction with the subscriber and updating subscriber data automatically. A change made on the publisher's side is automatically reflected on the subscriber's side as well.


 Real-Life Problems
Real-Life Problems
 Prep for Target Roles
Prep for Target Roles
 Custom Plan Duration
Custom Plan Duration
 Flexible Plans
Flexible Plans
2. What do you mean by BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)?
Beginners may see BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) as a type of Bluetooth that uses less power, uses less energy. BLE, or Bluetooth Smart, is a relatively new form of Bluetooth technology that consumes much less power and costs than classic Bluetooth while offering a similar range of communication. As shown in the following diagram, BLE is not a replacement for Classic Bluetooth and they both serve a specific marketplace.
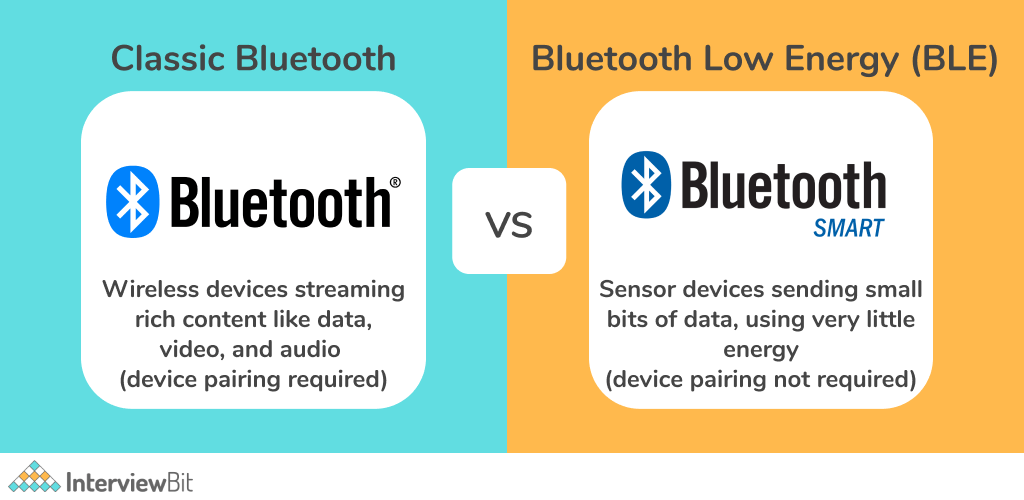
The Bluetooth Low Energy technology has been developed with the purpose of facilitating the IoT. Generally, the Internet of Things is about connecting devices with each other, usually via a wireless connection, such as Bluetooth low energy to allow them to communicate and share data. With its high energy efficiency, BLE has become a preferred and ideal choice for IoT. IoT enthusiasts and application developers have increasingly adopted Bluetooth LE to connect smart devices.
3. What are the different components of IoT?
IoT devices usually consist of four main components as follows:
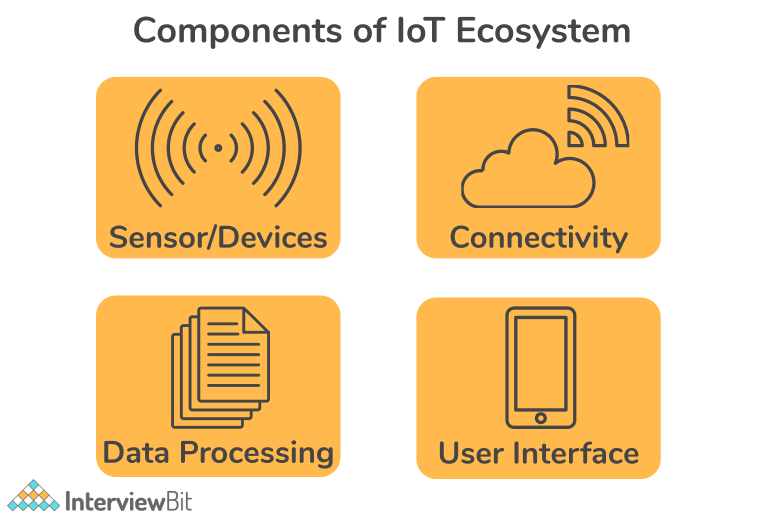
- Sensors: A sensor or device is an important component for gathering live data from the surrounding environment. The nature of this data can vary. This could be as simple as your phone having a temperature sensor, GPS, an accelerometer, or as complex as a live video feature on a social media platform. Sensors make it possible for IoT devices to connect to the real world and environment.
- Connectivity: Upon collection, all data is sent to a cloud infrastructure. This could be done by connecting the sensors to the cloud using a variety of communication mediums such as mobile or satellite networks, Bluetooth, WI-FI, WAN, etc. Various IoT devices use different types of connectivity.
- Data Processing: Once the data has been collected, and has reached the cloud, it is the responsibility of the data processors to process it. Data processing software can enhance IoT devices in a wide range of ways, from adjusting the temperature of the air conditioner to recognizing faces on mobile phones.
- User Interface: An IoT device interacts with a user through a User Interface. A user interface is the visible, tangible component of an IoT system that can be accessed by users. It involves presenting the information in a way that is valuable to the end-user. A well-designed user interface will simplify the experience for users and encourage them to interact more. Information needs to be made accessible to end-users in some way, like sending them alerts via notification, email or text message.
4. What are the advantages of IoT?
An IoT (Internet of Things) system is an advanced automation and analytics system that makes use of networking, big data, sensing, and Artificial Intelligence to provide a complete solution. It provides the following benefits:
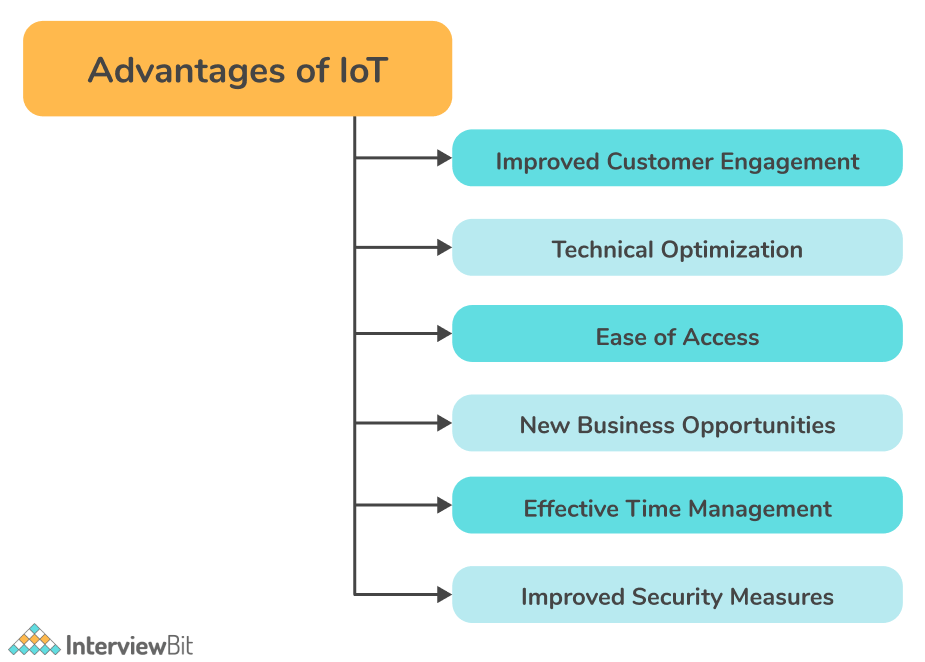
- Improved customer engagement: IoT facilitates a better customer experience by automating tasks. In a car, for instance, any issue will be detected automatically by sensors. It will be notified to both the driver and manufacturer.
- Technical optimization: IoT has improved technology and made it more efficient. It has turned even old "dumb" devices into "smart" ones by making them able to transmit data over the internet, facilitating communication with people and other IoT-enabled devices. For example, coffee machines, smart toys, smart microwaves, etc.
- Ease of Access: IoT has now enabled access to real-time information from (almost) any location. All you need is a smart device connected to the internet.
- Improved Insights: Currently we rely on superficial insights to make decisions, but IoT provides real-time insights that lead to more efficient resource management.
- New business opportunities: By collecting and analyzing data from the network, you can uncover new business insights and generate new opportunities while reducing operational costs.
- Effective Time Management: Overall, the Internet of Things can save you a lot of time. While we commute to work, we can read the latest news on our phones, browse a blog about our favourite hobby, or shop online.
- Improved security measures: Using IoT, access control systems can provide additional security to organizations and individuals. As an example, IoT technology in surveillance can assist in improving security standards in an organization, as well as identifying any suspicious activity.
5. What are the challenges or risks associated with IoT?
The following are some security risks associated with IoT:
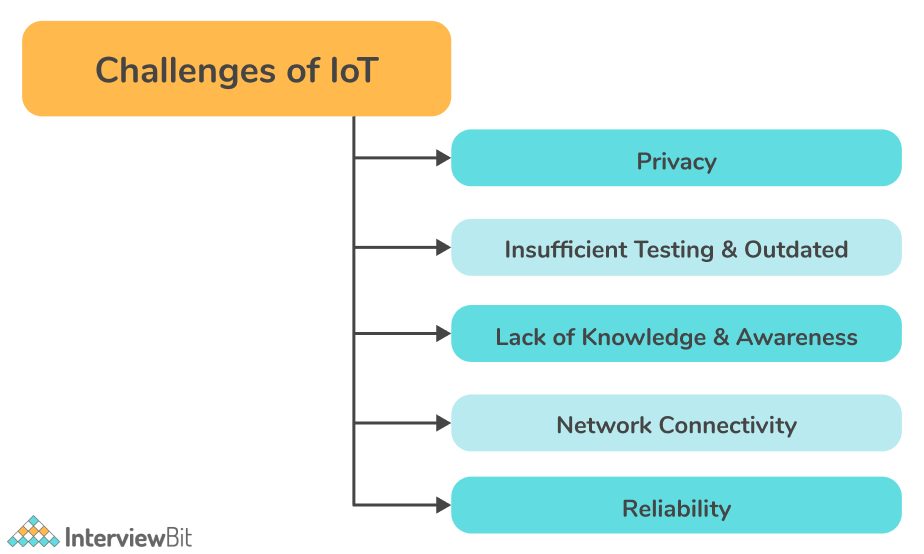
- Privacy: Connected IoT devices are vulnerable to hacking. Many IoT devices collect and transmit personal data over an open network without encryption, making it easy for hackers to access. Hackers may also use cloud endpoints to attack servers.
- Insufficient testing & Outdated product: In a fast-paced market like IoT, many companies or manufacturers rush to start releasing their products and software without doing enough testing. Many of them don't provide timely updates as well. Unlike other devices such as smartphones, IoT devices are not updated, which can leave them vulnerable to data theft. Thus, IoT devices should be tested thoroughly and updated as soon as new vulnerabilities are identified in order to maintain security.
- Lack of knowledge and awareness: Despite being a growing technology, people do not know much about IoT. A major security threat associated with IoT is the user's lack of knowledge and awareness of its capabilities. This poses a threat to all users.
- Network Connectivity: Network connectivity can be challenging for many IoT devices. Particularly if such devices are widely dispersed, in remote locations, or if bandwidth is severely limited.
- Reliability: Given the highly distributed nature of IoT devices, it can be difficult to ensure the reliability of IoT systems. Various conditions can affect the components that make up an IoT system, such as natural disasters, disruptions in cloud services, power outages, and system failures.
 Learn via our Video Courses
Learn via our Video Courses
6. What are different types of sensors in IoT?
In recent years, Internet-of-Thing sensors have gained importance for enhancing productivity, lowering costs, and improving worker safety. Sensors are devices that detect changes in the environment condition and act accordingly. They detect specific types of conditions (such as light, heat, sound, distance, pressure, presence or absence of gas/liquid, etc.) in the physical world and then generate a signal (usually an electrical signal) as a measure of their magnitude. Sensors commonly used in IoT systems include:
- Temperature sensors
- Pressure sensor
- Motion detection sensors
- Gas sensor
- Proximity sensor
- IR sensors
- Smoke Sensor, etc.
7. What are different layers of the IoT protocol stack? Write the classification of IoT protocols.
Internet of Things (IoT) protocols are ways of protecting data and ensuring it is exchanged securely between devices via the Internet. IoT protocols define how data is transmitted across the internet. By doing so, they ensure that data being exchanged between connected IoT devices is secure.

Classification of IoT Protocols-
| Layer | Protocol |
|---|---|
| Application layer |
|
| Transport layer |
|
| Network layer |
|
| Datalink layer |
|
| Physical layer |
|


 Real-Life Problems
Real-Life Problems
 Detailed reports
Detailed reports
8. What are different communication models in IoT?
In general, the Internet of Things is about connecting devices to the Internet, but how they connect is not always obvious. IoT devices connect and communicate through their technical communication models. An effective communication model shows how the process works and helps one understand how communication can be done. The Internet of Things (IoT) enables people and things (devices) to be connected wherever they are, using any network or service they like.
Types of communication models -
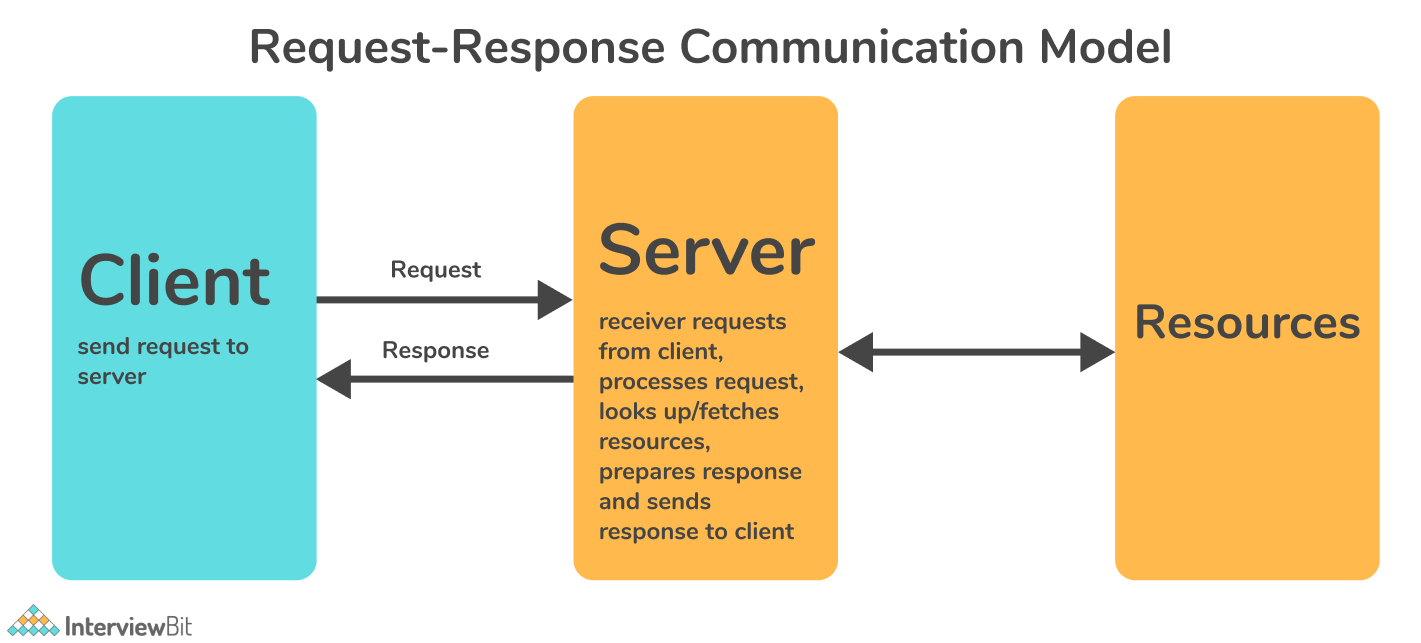
- Request-Response Model: This communication model is based on the client (IoT Device) making requests and the server responding to those requests. Upon receiving a request, the server decides what response to provide, fetches the requested data, prepares the response, and then sends it back to the client. This model is stateless because the data between requests is not retained, therefore each request is handled independently.
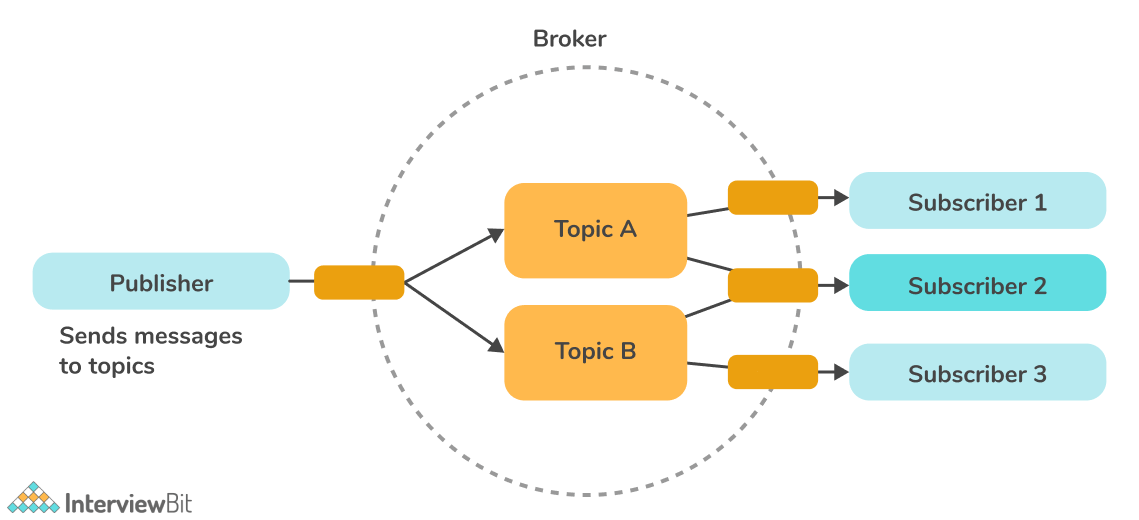
- Publisher-Subscriber Model: Publishers, brokers, and consumers are all involved in this communication model. Publishes are the sources of data that send data to topics. The broker manages the topics, and consumers (consume data from topics) subscribe to the topics. Publishers and consumers are unaware of each other. Upon receiving data for a topic from the publisher, the broker forwards it to all subscribed consumers. As a result, brokers are responsible for receiving data from publishers and sending it to the appropriate consumers.
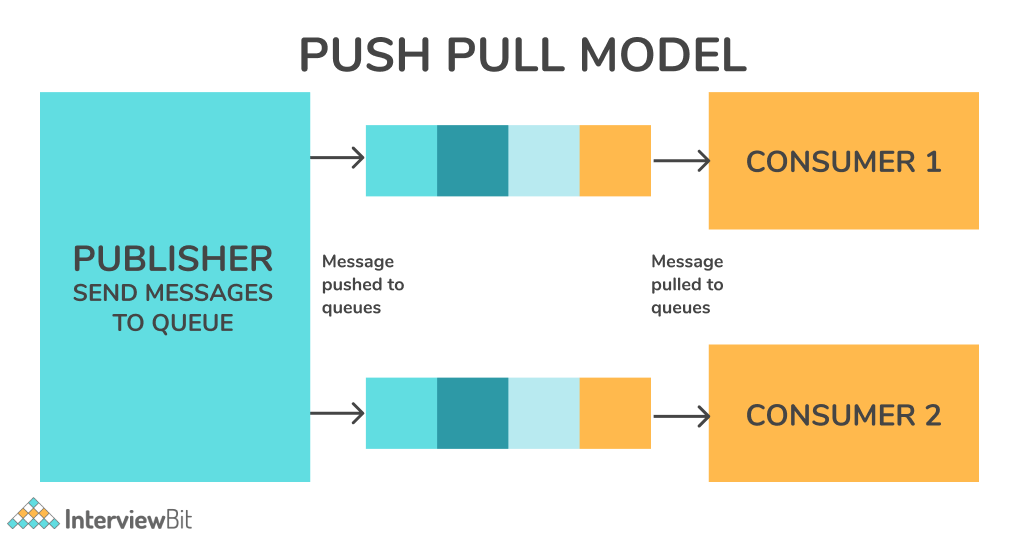
- Push-Pull Model: This communication model entails data producers pushing the data into queues, while data consumers pull the data from the queues. Neither producer nor consumer needs to know about each other. The queues help decouple the messages between the consumers and the producers. Also, queues act as a buffer when there is a mismatch between the rate at which producers push data and the rate at which consumers pull it.
- Exclusive-Pair Model: Exclusive pairs are full-duplex, bidirectional communication models developed for constant/continuous connections between a client and server. After a connection is established, clients and servers can exchange messages. As long as a client doesn't send a request to close the connection, the connection remains open. The server is aware of every open connection.

9. Write some of the most common IoT applications.
Following are some of the most common real-world applications of IoT:
- Smart Homes: Smart homes are one of the most practical applications of IoT. Though IoT is applied in smart homes at various levels, the best one combines intelligent systems and entertainment. Example: Set-top box that allows you to record shows from remote, an automatic lighting system, a smart lock, etc.
- Connect Health: Connected health systems allow for real-time monitoring and patient care. Patient data assists in better medical decisions. Also, IoT improves the power, precision, and availability of current devices.
- Wearables: Wearable devices have emerged as one of the earliest industries to deploy the IoT at scale. Various wearable devices are available today, such as Fit Bits, heart rate monitors, and smartwatches.
- Connected Cars: Connected cars use internet connectivity and onboard sensors to optimize their operation, maintenance, and passengers' comfort. Some of the leading automakers are working on bringing the next revolution to the car industry, including Tesla, BMW, Apple, and Google.
- Hospitality: By applying IoT to the hotel industry, a higher level of service quality is achieved. Various interactions can be automated by using electronic keys that are sent directly to the mobile devices of guests. Therefore, the IoT technology enables integrated applications to manage activities such as tracking guests' locations, sending offers or information about interesting activities, placing orders for room service or room orders, and automatically charging the room account.
- Farming: A variety of tools are being developed to deal with Drip Irrigation, understanding crop patterns, Water Distribution, drones for farm surveillance, etc. Farmers will be able to increase yields and address concerns using these methods.
10. Explain how IoT works.
Artificial Intelligence is at the core of IoT devices. The IoT consists of multiple components: sensors, a cloud component, data processing software, and cutting-edge user interfaces.
IoT systems consist of sensors/devices connected to the cloud via some form of connectivity. A Raspberry Pi equipped with a quadcore processor can be used as an "Internet gateway" for IoT devices. It is a card-sized computer using which you can control outputs with GIPO (general purpose input/output) pins as well as collect data about real-world conditions using sensors. A sensor gathers live data from the surrounding environment and sent to a cloud infrastructure. Once the data reaches the cloud, the software can process it and decide what action to take, such as sending an alert or automatically adjusting the sensors/devices without user intervention.
A user interface is used if user input is required or if they want to check in on the system. Adjustments made by the user are then sent inversely through the system - from the user interface to the cloud, and from the cloud back to the sensors/devices to make changes. As a result, a highly reactive and intuitive device is created which greatly increases automation.
11. Explain the characteristics of IoT.
The following are the most important features of IoT on which it operates:
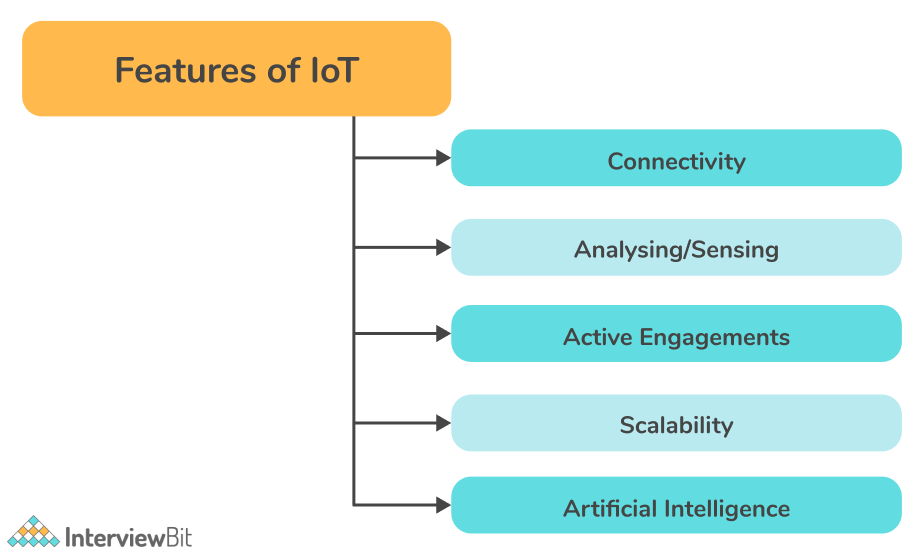
- Connectivity: Connectivity is the most important aspect of IoT. The IoT ecosystem (i.e. sensors, compute engines, data hubs, etc.) cannot operate properly without seamless communication among the interrelated components or objects. There are many ways to connect IoT devices including radio waves, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and Li-Fi.
- Analyzing/Sensing: Once all the relevant things are connected, the next step is to analyze data that is being collected and use it to build effective business intelligence. It is very important to extract knowledge from the generated data. A sensor, for example, generates data, but those data won't be of much use unless they are interpreted properly by us.
- Active Engagements: A lot of today's interactions with connected technology occur via passive engagement. Through IoT, multiple products, cross-platform technologies, and services work together on an active engagement basis. The use of cloud computing in blockchain enables active engagements among IoT components in general.
- Scalability: Each day, more and more elements are connecting to the IoT zone. IoT setups should therefore be able to handle massive expansion. The data generated as a result is immense, and it should be handled correctly.
- Artificial Intelligence: The IoT essentially makes things such as mobile phones, wearables, vehicles, etc., smart and enhances life by making use of data collection, artificial intelligence algorithms, and networked technologies. For example, if you have a coffee machine whose beans are going to end, it will order coffee beans from the retailer of your choice.
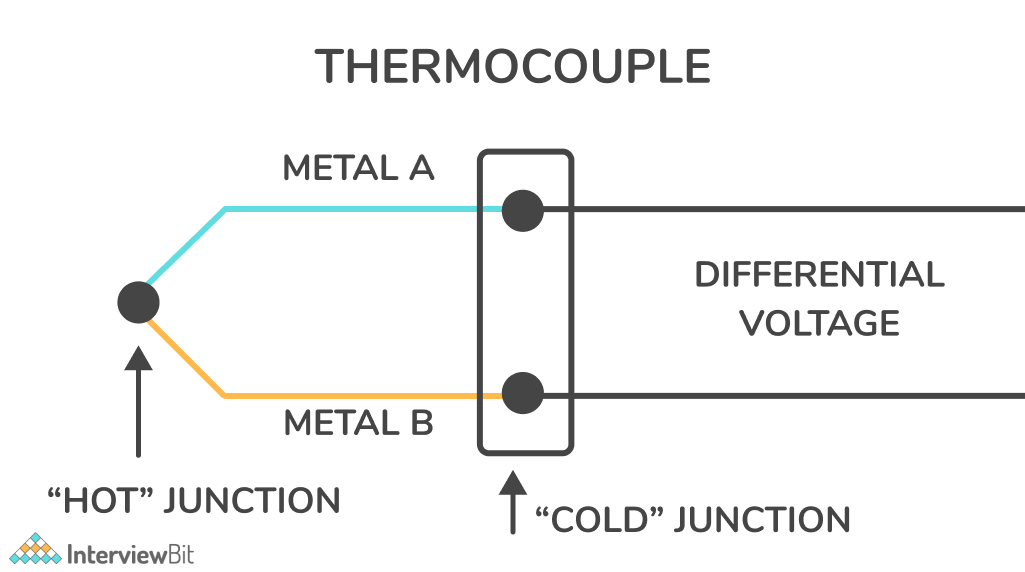
12. What is a thermocouple sensor?
A thermocouple is a sensor that measures temperature by coupling two metal pieces together. The temperature is measured at a junction between these two pieces of metal which are joined at one end. A small voltage is generated by the metal conductors, which can be interpreted to calculate the temperature. A thermocouple is a simple, robust, and cost-effective temperature sensor available in multiple types and sizes. Additionally, they measure a wide temperature range, making them suitable for a variety of applications, such as scientific research, industrial settings, home appliances, and so on.
13. Explain the term ‘smart city’ in IoT.
IoT technology has been a driving force behind the development of smart cities since their inception. IoT technology will continue to grow as more countries adopt next-generation connectivity, and it will have a greater impact on our lives. Connected sensors, lights, and meters are some of the IoT devices in smart cities that collect and analyze data. As a result, cities use this data to improve infrastructure, utilities, and other city services.
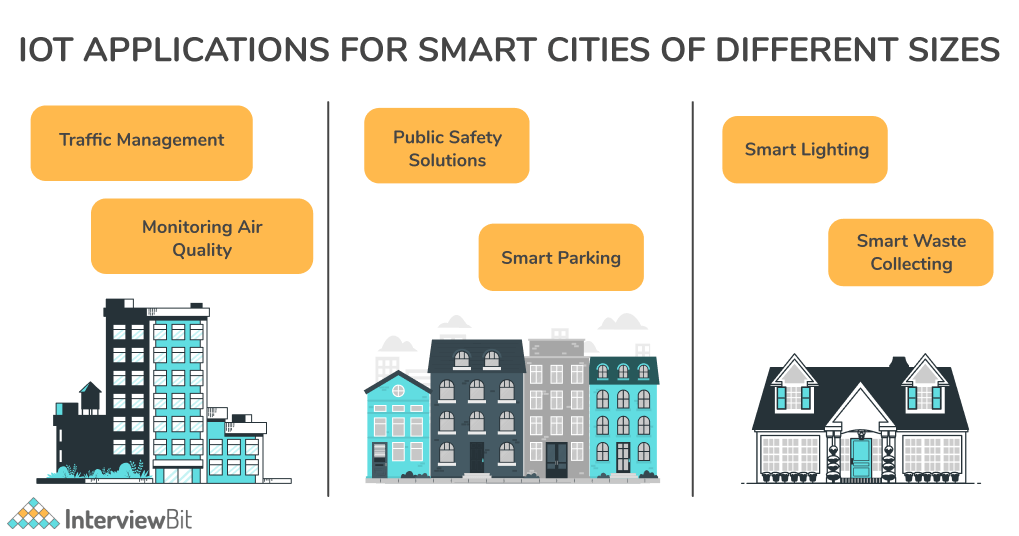
It is possible to create clever energy grids, automated waste management systems, smart homes, advanced security systems, traffic management mechanisms, water conservation mechanisms, smart lighting, and more with the help of the IoT. IoT has added a new layer of artificial intelligence and innovation to public utilities and urban planning, allowing them to be highly intuitive. These innovations have led to the emergence of smart homes and cities.
14. What do you mean by PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)?
Have trouble adjusting the brightness of the LEDs in your project? Changing the voltage of the power supply directly in the circuit isn't easy. In that case, you can use Pulse Width Modulation (PWM).
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), also referred to as PDM (Pulse Duration Modulation) refers to changing the amount of power that is delivered to a device. PWM is a technique for generating an analog signal from a digital source and is an efficient way to control the amount of energy delivered to a load without wasting any energy. PWM regulates voltage and is therefore used to control brightness in Smart Lighting Systems and also to control motor speed.
15. Explain Shodan.
Shodan (Sentient Hyper-Optimized Data Access Network) is a search engine similar to Google, but it does not search for websites, but rather maps and information about internet-connected devices/systems. Shodan is sometimes referred to as an IoT search engine. To put it simply, Shodan is an IoT tool used to identify Internet-connected devices. It keeps track of all the machines with direct Internet access.
Cybersecurity experts use Shodan as a tool to protect individuals, companies, and even public utilities against cyber-attacks. Shodan lets you search for any internet-connected device, and it will tell you if it is publicly available or not.
16. What do you mean by IoT Contiki?
Contiki is an operating system developed for IoT devices with limited memory, power, bandwidth, and processing power. Despite being minimalist, it still contains many of the features common to modern operating systems. Programs, processes, resources, memory, and communication can be managed with its help. Due to its lightweight (by modern standards), mature, and flexible nature, it has become a go-to operating system by many academics, researchers, and professionals.

17. Name some of the most suitable databases for IoT.
The following databases are suitable for IoT:
- InfluxDB
- Apache Cassandra
- RethinkDB
- MongoDB
- Sqlite
18. Explain sharding.
Sharding is the process of splitting very large databases into smaller, faster, and easier to manage pieces, called data shards. A shard is a small portion or chunk of a large data set. The principle of sharding is to split a logical dataset into multiple databases in order to store it more efficiently. In the case of a dataset that cannot be stored in a single database, sharding is necessary.
IoT Questions for Experienced
1. What do you mean by Raspberry Pi?
Raspberry Pi is a card-sized computer with features like General Purpose Input Output (GPIO) pins, WiFi, and Bluetooth that allow it to communicate, control, and connect to other external devices. Combining IoT applications with Raspberry Pi helps businesses embrace technology more effectively.
2. State the difference between IoT and M2M.
IoT (Internet of Things): It is referred to as a network comprised of interconnected physical objects that are capable of collecting and exchanging data. These devices contain embedded systems (software, electronics, networks, and sensors) that are able to collect data about the surrounding environment, transmit data over a network, respond to remote commands, or take actions based on data collected. The Internet of Things (IoT) is a subset of M2M (Machine to Machine) technology. In IoT, two machines communicate without human intervention, making it a part of M2M.
M2M (Machine to Machine): In M2M, devices communicate with each other directly via wired or wireless channels, without any human interaction. It enables devices to communicate and share data with each other without relying on the internet. Several applications of M2M communications are available, including security, tracking, and tracing, manufacturing, and facility management.
| IoT | M2M |
|---|---|
| It is a network of connected devices (via the Internet) that have the ability to collect, process, and transmit data automatically without human intervention. | It allows two or more machines to communicate directly and perform certain tasks without requiring human intervention. |
| In addition, IoT enables objects to interact with the internal and/or external environments, thereby influencing their decision-making. | The M2M model exhibits some degree of intelligence. Devices capture data and share it with other connected devices, forming an intelligent network. |
| It facilitates cloud-based communication. | End-to-end communication between devices/machines is supported. |
| In order to improve the end-user experience, data is shared between other applications. | Only parties communicating with each other have access to the data. |
| Internet access is usually required for devices to communicate and share data. | Devices don't usually require an Internet connection for communication. |
| Many machines are able to communicate over the internet. | The communication between machines is limited to one at a time. |
| Open API integrations are supported. | Open API integrations are not supported. |
| A number of Internet protocols are used, including HTTP, FTP, and Telnet. | Communication technologies and traditional protocols are used. |
3. What do you mean by IoT Gateway? What is the role of a gateway in IoT?
Devices such as IoT gateways enable communication between IoT devices, sensors, equipment, and systems. Basically, an IoT gateway is a central hub for all IoT devices. It connects the IoT devices to each other and to the cloud, converting communication among the devices and analyzing data to create useful information. Several critical functions are performed by an IoT gateway, including translating protocols, encrypting, processing, managing, and filtering data. As part of an IoT ecosystem, gateways sit between devices and sensors to communicate with the cloud.

IoT gateways are commonly used for the following purposes:
- Interconnecting devices
- Connecting devices to the cloud
- Transforming IoT communications
- Data filtering
- Reducing security risks, etc.
4. Explain WoT (Web of Things).
WoT (Web of Things) is an advancement of the Internet of Things by integrating smart things not only with the Internet (network) but with the Web Architecture (application). In short, the Web of Things (WoT) is aimed at facilitating the interoperability and usability of IoT. It is a web standard for enabling communication between smart devices and web applications.
5. What do you mean by MQTT (Message Queue Telemetry Transport Protocol)?
The Message Queuing Telemetry Transport protocol (MQTT) is a publish/subscribe message protocol designed for networks with limited bandwidth and IoT devices with extremely high latency (delay in data transmission). This messaging protocol is simple and lightweight, suited to devices and networks with low bandwidth, high latency, or insecure networks. It has been designed to reduce network bandwidth and resource requirements of devices and to ensure supply security. Furthermore, these principles are beneficial for IoT or M2M devices, since battery life and bandwidth are very important. Because MQTT is efficient and lightweight, it can be used to monitor or control a large amount of data. Nowadays, MQTT is used in a variety of industries, including automotive, manufacturing, telephony, oil and gas.

Publishes are the sources of data that send data to topics. The broker manages the topics, and consumers subscribe to the topics. Upon receiving data for a topic from the publisher, the broker forwards it to all subscribed consumers. As a result, brokers are responsible for receiving data from publishers and sending it to the appropriate consumers.
6. Explain Bluegiga APX4 protocol.
The Bluegiga APx4 is a low power wireless System-on-Module (SOM). It's an ideal development platform for developing gateways since it's equipped with integrated Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.0, ARM, and Linux. Wireless and Bluetooth low energy (BLE) can be used together without interference as they are compliant with coexistence protocols. Bluegiga Apx4 supports both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, and its 450mhz Arm9 processor provides smooth performance.
7. What is IoT device management and why do we need it?
Once installed, IoT devices may need to be updated or timely fixed. Occasionally, it must be replaced or repaired, resulting in downtime. The problem can be solved using IoT Device management, which can keep the devices in good shape. IoT device management involves provisioning, authenticating, configuring, monitoring, provisioning, and maintaining the connected devices and software's. Effective device management is vital for ensuring the health, security, and connectivity of IoT devices. In order to manage IoT devices, you need to meet the following four requirements.
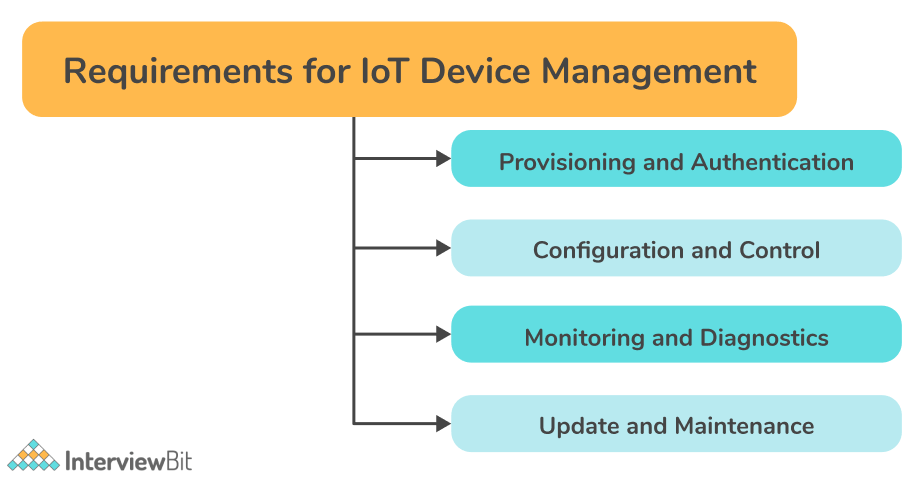
- Provisioning and Authentication: IoT devices can be attacked quite easily since their network can be accessed via the Internet. This problem is solved by provisioning and authenticating the devices. By provisioning, you modify the device from its off-the-shelf settings to those needed for it to work with your network. In order to prevent intrusions and safeguard proprietary information, authentication ensures only authorized devices are enrolled.
- Configuration and Control: It is always necessary to configure a new device before you can begin using it. It is also critical to control and configure devices after deployment to ensure certain aspects such as performance, security, and functionality. Implementing control capability will be easier this way.
- Monitoring and Diagnostics: The device may go down for a time when there are software bugs or certain other issues. To diagnose these issues, users must constantly monitor their devices. Device management assists in diagnosing these issues in order to resolve them quickly and efficiently.
- Updates and Maintenance: For a device to function flawlessly, it must be updated after it has been installed. This may involve adding new features. Good device management hinges on the ability to update and maintain the software of remote devices securely.
8. State the difference between IoT and IIoT.
IoT (Internet of Things): Any device that can connect to the internet and transfer data to a remote data server is termed the Internet of Things (IoT).
IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things): In the case of IoT devices used for industrial purposes, these devices are referred to as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). IIoT is the subset of IoT.
Difference between IIoT and IoT-
| IIoT | IoT |
|---|---|
| It supports industrial-oriented applications such as manufacturing, power plants, oil & gas, etc. | It supports customer-oriented applications such as wearables to robots and machines. |
| The focus is on large scale networks. | The focus is on small scale networks. |
| Both wired and wireless communication methods are utilized. | Typically, wireless communication methods are utilized. |
| A large amount of data is handled. | It can handle data ranging from medium to high. |
| This is a B2B (business-to-business) and is designed to increase efficiency and safety at production facilities. | This is B2C (business-to-consumer) and is designed to make the lives of consumers more convenient. |
9. Explain the meaning of Arduino.
Arduino is an open-source platform for building electronics projects using easy-to-use hardware and software. A microcontroller is the common feature of all Arduino boards. The microcontrollers on board are capable of reading inputs (e.g., light on a sensor, an object near a sensor) and converting them to outputs (drive a motor, ring an alarm, turn on an LED, display information on an LCD). It is possible to connect multiple devices and exchange data in real-time between them. It is also possible to monitor them remotely using a simple interface.
10. Explain sketch in Arduino and how will you reduce the size of sketch.
Arduino refers to a program as a sketch. In other words, it is a bit of code that is uploaded to and executed on an Arduino board. It is possible to reduce the size of the sketch by removing unnecessary libraries from the code and making it simple and short.
11. What is GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output)?
GPIO (General-purpose input/output) is a standard interface using which Raspberry Pi and other microcontrollers can connect to external electronic components/devices. These are basically programmable pins on an integrated circuit or board that allow digital input or output signals to be controlled programmatically.
12. State different between Arduino and Raspberry Pi.
We can use many different kinds of controller boards for our hardware projects. Arduino and Raspberry Pi are among the most popular.
Difference between Arduino and Raspberry Pi-
| Arduino | Raspberry Pi |
|---|---|
| Arduino is an open-source, programmable USB microcontroller. | It is a microprocessor-based minicomputer (SBC). |
| Arduino boards have a microcontroller that includes a CPU, RAM, and ROM. The Arduino Board has additional hardware for power supply, programming, and IO (Input/Output) connectivity. | The Raspberry Pi SBC (Single board computer) comes with everything you need to run a computer, from a processor, memory, storage, graphics driver, to connectors. |
| With Arduino, you can interface sensors and control LEDs and motors. | It works well for developing Python-based applications. |
| It has a simple hardware and software architecture. | On the other hand, Raspberry Pi boards have a complex architecture. |
| It is possible to build your own Arduino board using the open-source hardware and software files of Arduino. | Since the Raspberry Pi is not open-source, it cannot be used for this purpose. |
| It is used to run one single task at a time. | It can perform several tasks at once such as running software, web browsing, doing programming, etc.. |
13. State difference between IoT and WSN (Wireless Sensor Network)?
WSN (Wireless sensor network): It uses a network of dedicated sensors to monitor and record the physical conditions of the environment and to organize the recorded data at one central location. WSN: Sensor nodes connected without a wire to gather data.
IoT (Internet of Things): It is referred to as a network comprised of interconnected physical objects that are capable of collecting and exchanging data. These devices contain embedded systems (software, electronics, networks, and sensors) that are able to collect data about the surrounding environment, transmit data over a network, respond to remote commands, or take actions based on data collected. IoT: WSN + Any physical object (Thing) + IP address + Internet + App + Cloud computing + etc.…
14. Explain IoT GE-PREDIX.
GE (General Electric) Predix is a software platform for collecting industrial instrument data. This platform enables industrial-grade analytics for operations optimization and performance management via a cloud-based PaaS (platform as a service).
15. Name some of the wearable Arduino Boards.
The following wearable Arduino boards are available:
- Lilypad Arduino main board
- Lilypad Arduino simple
- Lilypad Arduino simple snap
- Lilypad Arduino USB
16. Explain IoT asset tracking.
"Asset tracking" entails tracking a particular asset and its location, whether it's a hammer, an X-ray machine, a vehicle, a shipping crate, or even a person. How does the IoT fit in here? Rather than manually tracking assets like a supervisor filling out a form when the asset arrives at a specific location, IoT tracking systems use sensors and asset management software to track things automatically. The assets are fitted with sensors, which broadcast their location over the internet on a continuous or periodic basis, and the software displays this information for you to see. Different types of IoT asset tracking systems transmit location information differently, such as via GPS, Wi-Fi, or cellular networks.
17. What do you mean by “Thingful”?
Thingful is a search engine for the internet of things (IoT). Using millions of publicly available IoT data resources, it provides a geographical index of real-time data from connected devices around the globe. With Thingful, IoT managers can detect patterns, identify anomalies, and analyze trends to solve problems.
Conclusion
A wide range of organizations can benefit from the internet of things. A key objective of the Internet of Things is to extend internet access from smartphones, laptops, and tablet devices to relatively basic devices such as toasters. As the Internet of Things has grown, there have been more opportunities in the fields of Mobile development, Cars, and household products that utilize and connect the Internet. With IoT technology pervading every aspect of our lives, an increased need for professionals trained to handle IoT devices has developed.
Hence, if you're considering an IoT interview, you've found the right place. In this article, we have compiled a list of the most frequently asked IoT interview questions with answers curated for both freshers and experienced professionals. Hopefully, these IoT interview questions will help you succeed in your next interview. Wishing you continued success.
Useful Resources:
IoT MCQ
What do things in IoT mean?
Which of these IoT blocks contains the Microcontroller Unit (MCU) or the Customer Chip?
Which of the following features should be part of an IoT sensor?
IoT stands for ___.
Which of the following is not an IoT communication model?
The Internet of things (IoT) can be integrated with which of the following separate domains?
In the IoT, what is the primary purpose of the Web of Things (WoT)?
IoT is an advanced automation and analytics system that deals with ___
What does the Active Engagement Features of IOT mean?
IoT devices are associated with data through which of the following methods?
Name the person who coined the term “internet of things”?
IoT protocols include which of the following?
What role does the gateway play in the smart grid architecture of IoT?












 Download PDF
Download PDF



















