SAP HANA Interview Questions
If you have been wondering What SAP HANA is, let me tell you, SAP Hana is a database with unique in-memory architecture and utilizes an easier data modelling system as compared to the regular database. SAP Hana is a column-oriented, in-memory database, that combines OLAP and OLTP operations into a single system; thus in general SAP HANA is an OLTAP system.
For most of the other databases that save data on the hard drive, SAP HANA saves it in memory. This implies that when you require the data, the system can browse it directly from the in-memory storage rather than calling it up from the hard drive. And this lets your system operate quicker when pulling the information you need.
Nevertheless, presently, SAP HANA has evolved more—beyond being just a database. In just a few years, SAP HANA has been acknowledged by its many clients as a versatile platform that has become the basis of an intelligent enterprise. Companies make use of SAP HANA to upgrade business processes, enhance digital insights, and streamline their IT domains. As a data foundation, SAP HANA disregards the hindrance of harbouring separate legacy systems and siloed data. It can cut data redundancy, hardware needs and data management costs as well.
SAP HANA explores live data for real-time business decisions, processing transactions, and analytics wherever they are located, employing cutting-edge data processing engines for business, spatial, text, graph, and series data. SAP HANA backs real-time analytics for observing telecommunications networks, detecting fraud and security, forecasting and profitability reporting, enhancing energy usage, and additional business processes.

More than a thousand certified appliance configurations from over thirteen leading vendors operate on SAP HANA. Different cloud suppliers deliver SAP HANA as an Infrastructure-as-a-Service, such as Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services. SAP also presents their own cloud services like SAP HANA Enterprise Cloud, a confidential managed cloud, and SAP Cloud Platform, a Platform-as-a-Service. SAP HANA is authorized to operate on Linux. The system is developed to handle both vertical and horizontal and horizontal scaling as SUSE Linux Enterprise Server is a reference development platform for SAP software, SUSE pairs with SAP to adjust the Linux OS for high-end performance. The recent ERP system from SAP's ERP software product line, SAP S/4HANA is designed on the basis of the ingenious SAP Hana database technology. It was founded as the fourth product generation in the year 2015. Clients can select between the SAP S/4HANA Cloud and the On-Premise solution.
SAP HANA Interview Questions for Freshers
1. State the contrast between SAP HANA and SAP S/4HANA?
A familiar term to all, SAP S/4HANA is an application developed to operate on the SAP HANA in-memory database platform. It was released in 2015, SAP S/4HANA is SAP’s most recent ERP (enterprise resource planning) and business intelligence offering, it uses technologies like machine learning, Artificial Intelligence, and cutting-edge analytics to simplify business processes.
From enhancing production planning in manufacturing to streamlining accounting processes in finance, SAP S/4HANA can change organizations’ business processes via smart automation. It can keep track and handle business resources, including products, and handle business commitments, like payrolls and purchase orders.
For example, in the case of retailers, it can deliver real-time stock availability to consumers, assist with more practical and efficient supply-chain management, and utilize predictive analytics to recognize and control delivery delays. SAP S/4HANA is the 4th version of SAP Business Suite and is developed to be more user-friendly than the previous versions. It can also easily resolve more complicated problems and handle much more data. Though SAP S/4HANA is cloud-native, it is not restricted to operating on the cloud. It has versatile ways of deployment, like via public, private, or hybrid cloud and on-premise.


 Real-Life Problems
Real-Life Problems
 Prep for Target Roles
Prep for Target Roles
 Custom Plan Duration
Custom Plan Duration
 Flexible Plans
Flexible Plans
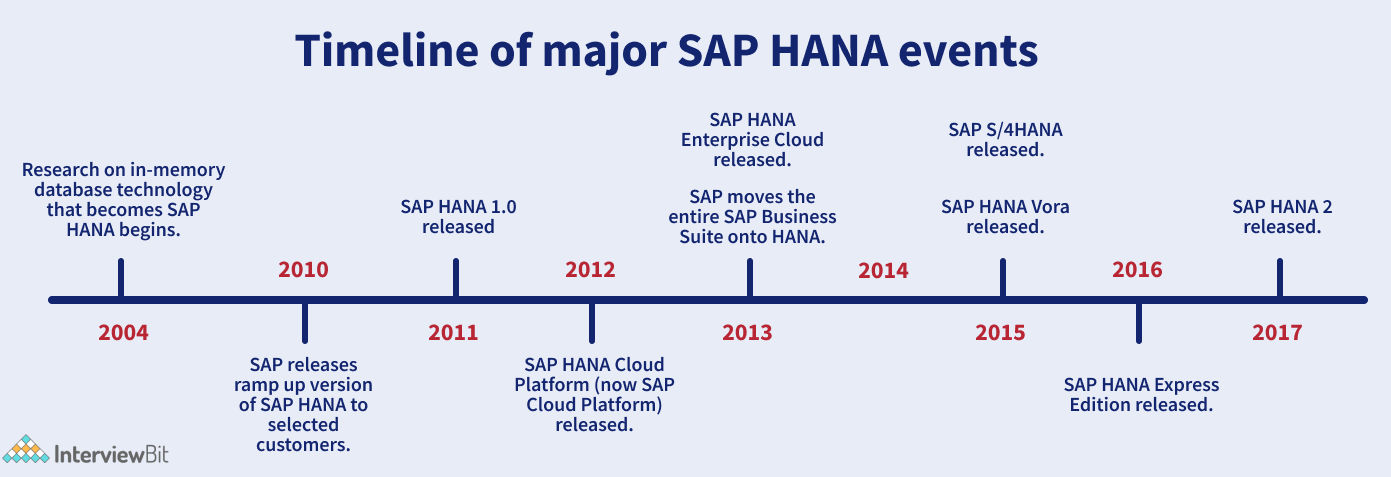
2. Describe the SAP HANA origins.
Commenced in the year 2006, SAP HANA was developed by SAP co-founder Hasso Plattner during the time he was a computer science professor posted at the Hasso Plattner Institute in Potsdam, Germany. The plan was to design a database that could work with a near-zero response time for the purpose of transactional and analytical data processing. Plattner desired a system that could respond to any potential business question in real-time. After many years of development at SAP, in October 2010, a prerelease edition of SAP HANA was presented to chosen clients. The first version of SAP, SAP HANA 1.0, was released on June 18, 2011.
SAP designed a cloud platform-as-a-service equipped with built-in support for SAP HANA in 2012. Later it renamed its Java-based server SAP NetWeaver Cloud to SAP HANA Cloud Platform (It changed its name in 2017 to SAP Cloud Platform and 2021 to SAP Business Technology Platform again). In 2013, SAP presented SAP HANA XS, a light app server implanted within SAP HANA that permitted application development.
In 2015, SAP declared a successor for the ERP ECC it had created in 1992. The new solution was to be anointed SAP S/4HANA and would possess numerous factors of existing ERP processes under one umbrella. Underpinning the latest solution? SAP HANA.
3. Mention the capabilities of SAP HANA?
SAP HANA features comprise:
- Multi-Model Processing – SAP HANA is competent in preserving and processing numerous types and collections of data in various formats, like graphs, tables, and documents.
- Hybrid Processing – HANA can work both as a transactional and an analytical database. It can process both types of requests on a single data set concurrently.
- App Development Tools – SAP HANA is packed with a combination of application development tools, like Eclipse and Web IDE. Administrators can streamline their personalized application's architecture by operating with coding languages that best suit their requirements and objectives.
4. How Much Does SAP HANA Cost?
The price of an SAP HANA license relies on per-gigabyte use. SAP takes into consideration additional aspects, involving the present market price of competitor databases while delivering a quote for SAP HANA. The total price depends, however, on each business’ needs. A few things to consider when analyzing whether to incorporate SAP HANA or not are execution needs, adaptability, scalability, and whether or not full control over the instance is required or just want to take advantage of in-memory computing.
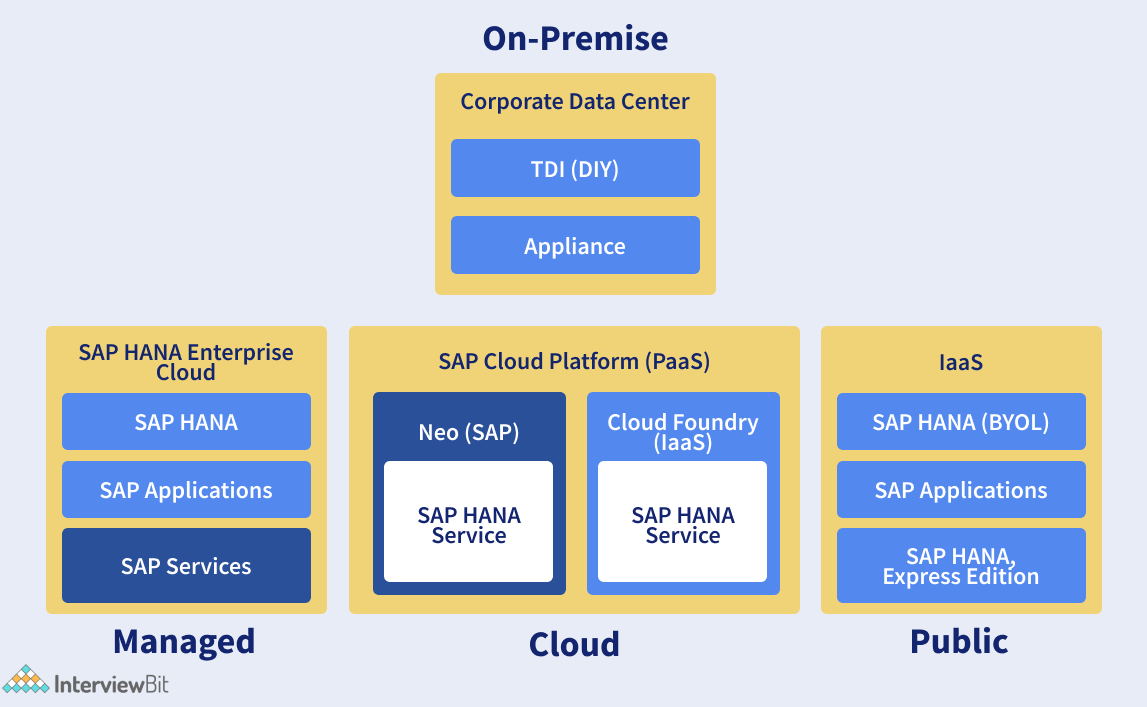
5. Describe the types of SAP HANA Installations.
Once a business has chosen to move to SAP HANA, it can select from one of three deployment options.
-
On-Premise:
- Users get an easy signature file by buying a key from the SAP Support website in an on-premise implementation.
-
Cloud:
- There are two kinds of cloud implementations known as public or private. Those who are getting their license to the public cloud would take the same steps as those functioning on-premise installations.
- Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform would act as a host to the cloud instance of SAP HANA. On the other hand, a private cloud implementation lets clients license an SAP HANA database on a cloud that is impressive to them. This can be a limited server hosted by a third party, or a server physically hosted by the company renting SAP HANA.
-
Two-Tiered (Hybrid):
- In a two-tiered implementation, companies run on both on-premise and cloud versions of SAP HANA. There are various grounds why this may be desirable, such as a wish to analyze the option of a future full-cloud deployment while currently operating an on-premise deployment.
 Learn via our Video Courses
Learn via our Video Courses
6. What are the SAP HANA use cases?
SAP HANA backs diverse use cases for real-time analytics. Some examples are:
- Optimizing telecommunications
- Supply chain optimization
- Retail sales optimization
- Fraud detection
- Profitability forecasting
- Energy use optimization
SAP HANA has demonstrated its value in the sector of data management and application development. It retains more than 1000 certified applications that run predominantly on SAP HANA. It is regarded as one of the few database systems that you can rely on when networks are performing best. SAP HANA is also certified for the Linux operating system (OS).
7. Elucidate the Benefits of SAP HANA.
It is a well-regarded fact that SAP HANA is more than just a database used for storing and serving data.
Here are six of the top advantages of operating working SAP HANA:
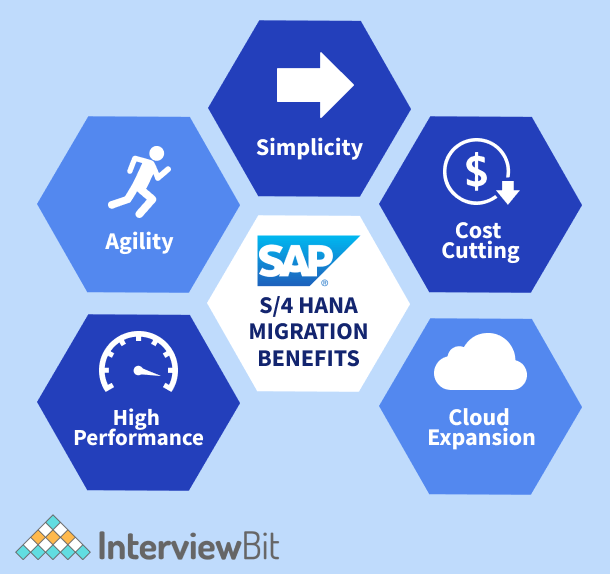
- Easily Handle Big Data: With SAP HANA, you can handle big chunks of data from any source. Also, SAP HANA’s inbuilt machine learning and cutting-edge analytic abilities permit you to include unstructured data, such as predictive, text, spatial, event streams, and time series, enabling your business to arrive at better decisions.
- Gain Real-Time Analytics: The in-memory technology of HANA dramatically decreases the time it takes to derive the most comprehensive reports. With HANA's accelerated business intelligence functionalities, you will be able to process data in near real-time, helping you make business decisions much more decisively.
- Scalability: SAP HANA utilizes dynamic tiering, which indicates that data that’s operated repeatedly stays in memory whereas less-used data shifts to disk when there is less space. Not only is this an incredibly economical way to handle large data volumes, but when you take HANA’s state-of-the-art compression and columnar storage into consideration, it can cause a data footprint decline of anywhere from 3 to 5 times.
- Single Source of Truth: A considerably simple advantage of SAP HANA is that it provides you with the capability to minimize your data silos by combining transactional and analytical data on a single solution. One source of truth allows us to discard errors, reduplication of data, and a lot of additional issues that take time and energy to fix.
- Flexibility and Versatility: One of the most multi-faceted data solutions, you can deploy SAP HANA in a public or private cloud, in numerous clouds, or in a hybrid scenario. It also backs hybrid transactional and analytical processing, along with multiple other types of data.


 Real-Life Problems
Real-Life Problems
 Detailed reports
Detailed reports
8. What are the shortcomings of shifting to SAP HANA?
Now that you have checked the advantages of SAP HANA, you might be more confident to execute the migration. Nonetheless, before choosing to make the transition, you also have to be mindful of the shortcomings you’ll encounter during the process. Here are some of the disadvantages you should be cautious about while shifting to SAP HANA:
- Planning: Pain Points: Many companies fail to recognize the actual problems of their existing database infrastructure. Therefore, they miss the scope of the project. This results in wasted endeavours and resources. Without a concrete project goal and precise estimation of project expense, you will not have an accurate roadmap to digital transformation, thus it can negatively affect your Return on Investment (ROI).
- Technical Issue: Code Conversion: Other shortcomings emerge from the technical aspect of the migration. If your system is still operating with a non-Unicode language, then it can cause a major challenge to migrate to SAP HANA. SAP HANA only backs the Unicode system, so most of the new SAP NetWeaver technology and SAP applications will be available only in Unicode. Thus, the requirement for Unicode system conversion has to be executed mindfully before moving to SAP HANA. Many companies are not aware of this knowledge of conversion, as a result, leads to system failures and waste.
- Execution: Downtime: Like in any other migration project, it all begins with an initial migration in the sandbox for the purpose of testing. Post which, the migration moves to Development and Quality before eventually advancing into Production. The primary problem when shifting to Production is the downtime as the consumers cannot access the system during this process. There might be a greater possibility of system failures during the migration if you do not pre-test the new database system comprehensively. It would lead to more significant downtime or worse, failures would be detected too late, leading to even lengthier outages.
9. Mention 10 Other Fundamental SAP HANA Terms.
There are a few essential SAP HANA terms you should also be acquainted with in addition to the details mentioned above. Let us take a look at those:
- Apache Hadoop: An open-source, external, software library employed for accumulating and processing big data to expand data storage and decrease processing times. It is often used in tangent with SAP HANA.
- SAP BW/4HANA: This is a data warehousing solution, which relies on SAP S/4HANA. The contemporary counterpart of SAP Business Warehouse (SAP BW).
- SAP HANA Application Associate Exam: An exam that lets anyone who wants to display knowledge of SAP HANA have the possibility to demonstrate their expertise and attain SAP certification.
- SAP HANA Cloud Services: An edition of SAP HANA made to operate in the cloud. Revealed at SAPPHIRE in 2019, it is presently under development.
- SAP HANA cockpit: The chief system administration instrument for SAP HANA 2.0.
- SAP HANA Data Management Suite: It is a data management, orchestration, and governance solution comprising SAP Data Hub and SAP HANA.
- SAP HANA Data Warehousing Foundation: A tool utilized for constructing an enterprise data warehouse for SAP HANA with the help of SAP SQL programming language.
- SAP HANA, express edition: Designed to be operated with a smaller memory footprint and in the cloud, it is a specialized edition of the SAP HANA database.
- SAP HANA Predictive Analysis Library (PAL): A compilation of processes in the Application Function Library utilized to incorporate predictive modelling.
- SAP HANA Studio: This is another tool, which is used to interact with an SAP HANA system and handle security. As of SAP HANA 2.0, SAP HANA Studio has been deprecated.
10. Describe briefly what is SAP HANA?
One of the most favoured analytical products around, SAP HANA is used by many high-end companies like HPE, IBM, and Dell, all these companies own products and services optimized for the software.
German software giant SAP's flagship product, SAP HANA is an in-memory database platform that scrutinizes data at elevated speeds by processing information saved in RAM, rather than acquiring it from the hard disk or SSD. This way it lets other programmes use extended amounts of data much more quickly. HANA, a proprietary product denoted a 'high-performance analytic appliance' in 2011, it was first launched and HANA 2017 was released six years later. The system can support petabytes of data in-memory while returning results within a second.
11. Mention the differences between BWA (Business Warehouse Accelerator) and SAP HANA. Also, state how is SAP HANA operating presently?
- Business Warehouse Accelerator or BWA: The in-memory accelerator for Business Warehouse is BWA. The primary goal of BWA is to enhance the query performance of SAP Net Weaver BW. BWA is solely designed to speed-up BW queries, it also decreases the time of data acquisition by enduring the copies of the info cube.
-
SAP HANA: It is an in-memory database. In this platform high-performance, analytic reports and applications thrive. Another important thing is that data can be loaded in SAP HANA from SAP and non-SAP Source System via DXC, SLT, Sybase, and BODS. This can be viewed with the help of SAP BO/BI, Crystal Reports, or Excel.
Presently, SAP HANA is operating as an in-memory database for SAP BW. And now SAP HANA is capable of improving the overall execution of SAP Net weaver BW.
12. Explain SAP HANA Architecture in short?
The SAP HANA database is created in C++ and operates on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server. SAP HANA database comprises numerous servers and the most significant feature is the Index Server. SAP HANA database includes Statistics Server, Name Server, Index Server, XS Engine, and Preprocessor Server.
13. What is a text table in SAP? What is the need of designing a text table?
So, table A is a text table of table B given the key of A consists of the key of B and an extra language key field (field of data type LANG). Table A may, thus, include explanatory text in different languages for every key entry of B.
- Objective: Text Join is utilized to fetch the depiction based on the consumer's session language. Once we enforce the text join in SAP HANA, it finds out the consumer's language automatically and provides a definition in that language.
14. Does SAP HANA only operate under a SAP system?
The platform is best suited for SAP and non-SAP applications- what is feasible actually relies on the license selected. The SAP HANA Runtime Edition is developed for only SAP applications. With the help of these applications, work can be executed at the application level. This is not the same while selecting the SAP HANA Full-Use License: This enables organizations with all of the functionality of the platform. Work can also be executed at the database level.
SAP HANA is appropriate for third-party applications. HANA backs different standards, like the commonly used programming language SQL. Thus, deeper programming knowledge in ABAP is not needed. Without ABAP, tables can also be designed, supported, and readout. Lastly, SAP HANA also backs SAP UI5, which is a framework for designing individual apps suited for businesses having user-friendly interfaces like, based on Fiori.
15. Describe what is schema mapping?
Schema mapping is accomplished when the physical schema within the target system is not identical to the physical schema in the source system. Assuming we are transferring components from DEV (Development System) to PROD (Production System). The tables in Development System live in DEV_SCHEMA and the exact tables reside in the PROD system in the PROD_SCHEMA schema. If an attribute view is moved from DEV to PROD, it will not function as the schema name is described in the definition of attribute view. For the promoted objects to function in PROD, schema mapping ought to be set up in the target system. In this situation, the schema mapping to be designed is:
- Authoring Schema
- Physical Schema
- DEV_SCHEMA
- PROD_SCHEMA
SAP HANA Interview Questions for Experienced
1. Define SAP Collections Insight?
SAP Collections Insight backed by SAP HANA lets you access real-time mobile association and collections account information at any given place and time. It allows you to fix collections issues, better manage your collections efforts, tighten business relationships, and get paid quickly.
2. State the contrast between Raw Data, Distinct values, and Analysis when you are accomplishing the Data Preview?
- Raw Data: It shows all attributes alongside data in a tabular format.
- Distinct Values: It shows all attributes alongside data in a graphical format.
- Analysis: It depicts all measures and attributes in a graphical format.
3. State SAP HANA backs Massively Parallel Processing?
With the accessibility of Multi-Core CPUs, more elevated CPU execution speeds can be attained.
Furthermore, HANA Column-based storage makes it effortless to perform operations in parallel with the help of multiple processor cores.
Data is already vertically partitioned In a column store. This implies that operations on various columns can readily be processed in parallel. If numerous columns ought to be explored or aggregated, each of these processes can be assigned to a separate processor core. Additionally, by dividing the column into numerous sections that can be processed by various processor cores, operations on one column can be parallelized. With the help of the SAP HANA database, queries can be accomplished rapidly and parallelly.
4. What are the different types of Input parameters supported?
The following types of Input parameters are supported.
- Currency: This can be used during currency conversion where the end-user should mention a source or target currency.
- Date: It is Used to get back dates from the end-user with the help of a calendar type input box.
- Static List: This can be used during the time the end-user needs to have a setlist of values to select from.
- Attribute Value: If an Input Variable owns this type, it serves a similar purpose as a normal Variable.
- Note: If none of the above is applicable you do not have to mention an Input Variable type. It can be left blank.
5. Name the various compression methods in HANA?
- Run-length encoding
- Cluster encoding.
- Dictionary encoding.
6. What happens when an object is activated in HANA?
When an object is activated, it becomes accessible for reporting and analysis. After the view has been successfully activated, a run-time object is built in the _SYS_BIC schema.
For instance, let’s say there exists a calculation view CV_VIEW1 in package “MyPackage”. After this view is activated, a run time object (column view) will be developed in _SYS_BIC schema having the name “MyPackage/CV_VIEW1”. This column view is implemented while performing the data preview of the calculation view.
7. State the difference between Activate and Redeploy?
- Activate – Implement the inactive objects.
-
Redeploy – Implements the active objects in any of the scenarios:
- If your runtime object becomes corrupted or deleted, and you need to build it again.
- If your runtime problems while object activation, and the object status shows active.
8. Mention the kinds of schema in HANA?
In HANA, there are 3 kinds of schemas.
- User-Defined Schema: These are developed by the user, DBA or System Administrator
- SLT Derived Schema: During the configuration of SLT, it develops the schema in the HANA system. All the tables imitated into the HANA system are included in this schema
- System Defined Schema: System Defined schemas are provided with the SAP HANA database and include information on the HANA system. _SYS_REPO, _SYS_BIC, _SYS_BI, _SYS_STATISTICS are the system schemas.
9. If the tables of a schema are implemented to create modeling views then why is it essential to grant SELECT privilege to user _SYS_REPO?
If tables of a schema for example SCHEMA_ABC are implemented to create the modelling views, then the following SQL statement must be performed before starting any such modelling views.
GRANT SELECT ON SCHEMA SCHEMA_ABC TO _SYS_REPO with the option of GRANT
Consider _SYS_REPO as “the activation guy”. It takes your models and makes the required runtime objects from them. Thus user _SYS_REPO requires the allowance to choose YOUR tables/views. (If _SYS_REPO user is unable to decide on the tables added in the from-clause of the view-definition, it will fail to describe that view). If different customers require to choose this view (It is quite obvious this is always the scenario, else the views would not make any sense), then _SYS_REPO ought to have the extra allowance to grant the selection further (with the grant option).
After all your models that access data in your schemas has been activated, _SYS_REPO wants to offer you and other users read access to the activated models.
10. Define what is a modeling studio?
- Modelling studio in HANA executes numerous tasks like:
- States which tables are saved in HANA, the first part is to obtain the meta-data and then prepare data replication jobs
- Handle Data Services to get through the data from SAP Business Warehouse and other systems
- Handle ERP instances connection, the existing release does not support connecting to different ERP instances
- Employ data services for the modelling
- Accomplish modelling in HANA itself, essential licenses for SAP BO data services.
11. Mention the advantages of owning a collections management solution backed by SAP HANA?
SAP HANA can gather huge amounts of elaborate data from source systems, into the memory directly, where mapping, synchronization, and translation, can be accomplished in real-time, without the requirement for data duplication and pre-aggregations. This allows users to plan rapidly and iteratively using their complete, detail-level data-spending less time collecting and assembling data and more time making the critical decisions that drive their business.
12. What are the different user parameters that can be defined in the Semantic layer?
- Measure and Attribute
- Hierarchies
- Parameters/Variables
- New Calculated Column.
13. Define the Hierarchy? What are the kinds of hierarchy supported in HANA?
To structure and specify the relationships among attributes in a modelling view. Hierarchies are implemented.
Companies describe hierarchies for classification of information, letting roll-up and drill-down analysis. For instance, a sales company might assign a salesperson to a country and a country is assigned to a region. Then the sales data can be calculated and scrutinized by region, country, or salesperson.
There are two kinds of hierarchies:
- Level Hierarchies are rigid hierarchies, where you can access the root and the child nodes in the defined order. For instance, organizational structures.
- Parent/Child Hierarchies are regarded as value hierarchies, i.e, hierarchies obtained from the value of a node. Such as a Bill of Materials (BOM) includes Assembly and Part hierarchies, and an Employee Master record includes Employee and Manager data. The hierarchy can be analyzed on the basis of a selected parent, also, there are scenarios where the child can be a parent.
14. What’s the objective of Generating Time Data?
Under Quick Launch, Generate Time Data option allows the consumer to develop the Time data so that it can be employed for designing the Time-based Attribute Views.
When you select Generate Time Data, you will be supplied with two options:
- Gregorian: Mostly the data will be rendered based on From and To years alongside the granularity - Second, Minute, Hour, Day, Month mentioned.
- Fiscal: In this circumstance, the time data will be rendered based on the variant described (some organizations may use their time).
Standard tables T005T, T005U, T009, and T009B in SAP HANA are needed if you opt for the Fiscal type.
Conclusion
This article is all about learning about SAP HANA and the probable interview-related questions and answers you should be aware of. We hope the article will help you nail your SAP HANA interview.
Useful Interview Resources:
15. Mention the difference between the Variable and Input parameter in HANA?
- Variables are attached to columns and are employed for filtering with the help of WHERE clauses. They can just include the values available in the Columns they associate to. Variables do not affect the performance,
- HANA Input parameters are used to drive the execution on the basis of user input. Occasionally, you might not want a variable to simply limit the data of a view. But you might also want to take input from the customer and process it, returning dynamic data on the basis of the user selection. Input Parameters makes this achievable.
16. Cite the function of the persistence layer in SAP HANA?
SAP HANA contains an in-memory computing engine and the data is available right away without the need for any backup. During hardware failure or power cutoff, to evade the chance of misplacing data, the persistence layer acts as a saviour and saves all the data in the hard drive that is not volatile.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How can I prepare for SAP HANA interview?
Here are some more things to keep in mind:
- Be thorough with SAP HANA
- Market your education
- Demonstrate your experience
- Avoid talking numbers
- End on a strong note.
2. Is SAP HANA difficult to learn?
Yes, a newbie can explore SAP HANA. But getting the right opportunity in the field of SAP Hana becomes a little challenging. You should be too strong in SAP HANA, as well as SQL & Analytics. If you are well versed with any traditional database and functionality then it will help you comprehend HANA.
3. Is SAP HANA in demand in 2022?
Yes, and it will stay in demand in the coming future because of these reasons:
- Best reliable ERP
- Each big corporate cannot depend on tally or other means of ERP
- Very efficacious and secure means of ERP
- Fewer chances of scams and irregularity in Sap
- No unauthorised access in ERP.
4. What is the salary of SAP HANA Developer in India?
Salary ranges from 7L per annum above 15L per annum depending on the experience.
SAP HANA MCQ Questions
A SAP HANA Modeler is attempting to activate an Analytical view and the error message- insufficient privilege pops up. Which user should be given the access to Schema and tables employed in HANA view to activate the view?
A SAP HANA programmers want to construct an HTML application and host it on a web server within HANA. Name the below-mentioned component in HANA architecture that can be used by Web applications to avail HANA database?
How many viewpoints can be found in SAP HANA Studio (SPS03)?
In which language is the SAP HANA database developed?
SAP HANA system can be developed within _____
To obtain multiple measures from various tables, which of the below is the most suitable view type to be utilized in HANA Modeling?
What approach is employed to extract tables from the ECC server in real-time?
Which are the components of SAP HANA Studio?
Which migration method in SAP HANA lets you export numerous packages to a remote HANA server?
Which viewpoint is utilized to build joins?












 Download PDF
Download PDF



















